Reflecting on developing literacy for early readers.
I have started to read a lot to support students that are early readers. One thing that I have learned is that exposing students to a variety of texts and strategies supports literacy development. Very important factors to supporting early readers are learning how students learn to read words.
Information from
Cain, K. (2010). Learning to read words. In K. Cain, Reading Development & Difficulties (Ch. 4, pp. 67-94). Toronto: Wiley.
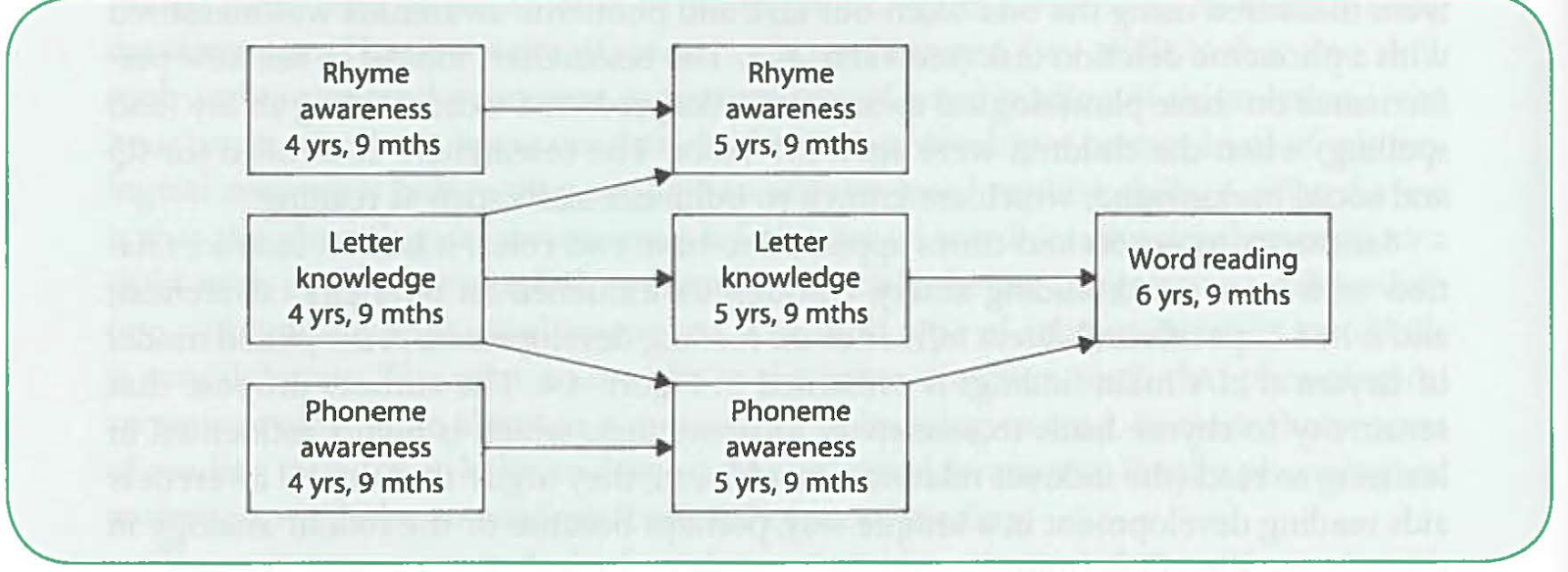
Information from
Cain, K. (2010). Learning to read words. In K. Cain, Reading Development & Difficulties (Ch. 4, pp. 67-94). Toronto: Wiley.
Sight word
When a reader sees a familiar word on a page or a computer screen, a word that they have read several times previously, their memory for that word is activated.
Phonological
When readers see an unfamiliar word, they can try to read it by sounding out the individual letters and blending them
Analogy
To read by analogy, readers use information from similarly spelled words that they
know in order to pronounce unfamiliar words, for example using knowledge about
the pronunciation of a familiar word such as table to pronounce a new word, such
as fable.
Prediction from context
To 'read' an unfamiliar word, readers may use several sources of contextual support.
These include memory for the text read so far, knowledge about the topic, and knowledge
about syntactic constraints.
Print awareness- How to read a text. Example start on the left and move right.
Letter knowledge-
Phonological processing skills-
Phonological awareness-Phonological awareness refers to the ability to identify and manipulate the sound structures of words.The largest unit of division is the syllable.The largest unit of division is the syllable: metaphysical has five syllables, 'met - a - phy - si - cal'. Syllables can be subdivided into intrasyllabic units. The most common intrasyllabic units studied in reading research are onsets and rimes. An onset is the initial consonant or consonant cluster,
for instance the I m/ sound at the beginning of met or the I tr I sound at the beginning of train. A rime is the vowel and any subsequent consonants in the syllable, for example et and ain. Phonemes are the smallest unit of interest. There are three phonemes in met: 1m/, I e/ and / t / , and four in train: It/, /r/, /ail and /n/.
Rapid automatized naming- Rapid automatized naming (RAN) tasks require the participant to name arrays of familiar items such as letters, digits, colours and objects, as quickly as possible.
Verbal short-term memory- Verbal short-term memory tasks involve the repetition of verbal stimuli, such as nonwords, or the recall of lists of words or digits.
Comments
Post a Comment